Quectel HighSpeed USB Composite Device Driver 5.0.1.3 for Windows 10 Creators Update 64-bit. SAMSUNG Mobile USB CDC Composite Device Driver 2.12.4.0 for Windows 10. Also, make sure your MTP device is connected to your PC, otherwise it won’t show. Right-click it, and choose Update Driver Software. Select Browse my computer for driver software. Click on Let me pick from a list of device drivers on my computer. From the options presented, select MTP USB Device, and click next. Follow the installation wizard. Free drivers for HiTi S420. Found 4 files for Windows 7, Windows 7 64-bit, Windows, Mac OS 10.x, Mac OS X, Mac OS X 10.6. Select driver to download. Select Update Driver. If Windows doesn't find a new driver, you can try looking for one on the device manufacturer's website and follow their instructions. Reinstall the device driver. In the search box on the taskbar, enter device manager, then select Device Manager. Right-click (or press and hold) the name of the device. Hiti card printer cs-200e driver for windows download - we are a leading solution provider for your id card printing needs, and take care to ensure that you are supplied the right package at the right price. We are not been tested and other trusted sources. 9, pursuant to dye-sub printing. Hiti printer drivers download by hiti.
-->For certain Universal Serial Bus (USB) devices, such as devices that are accessed by only a single application, you can install WinUSB (Winusb.sys) in the device's kernel-mode stack as the USB device's function driver instead of implementing a driver.
This topic contains these sections:
Automatic installation of WinUSB without an INF file
As an OEM or independent hardware vendor (IHV), you can build your device so that the Winusb.sys gets installed automatically on Windows 8 and later versions of the operating system. Such a device is called a WinUSB device and does not require you to write a custom INF file that references in-box Winusb.inf.
When you connect a WinUSB device, the system reads device information and loads Winusb.sys automatically.
For more information, see WinUSB Device.
Installing WinUSB by specifying the system-provided device class
When you connect your device, you might notice that Windows loads Winusb.sys automatically (if the IHV has defined the device as a WinUSB Device). Otherwise follow these instructions to load the driver:
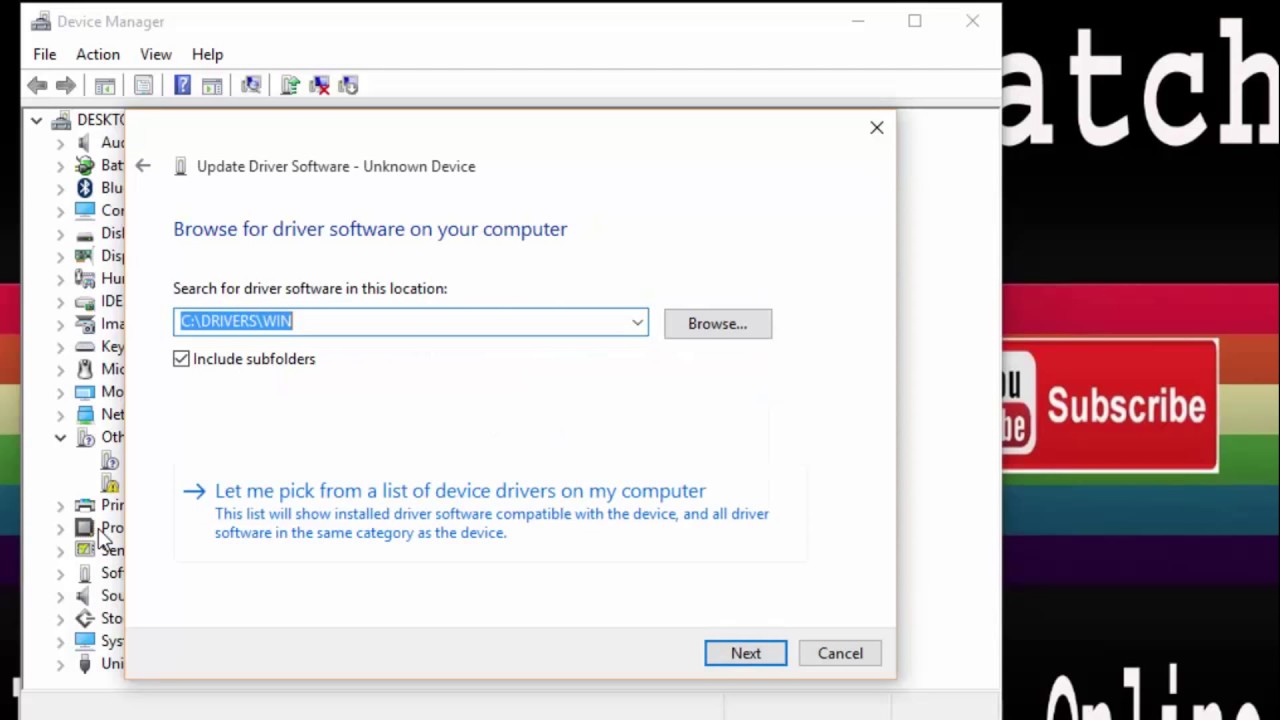
- Plug in your device to the host system.
- Open Device Manager and locate the device.
- Select and hold (or right-click) the device and select Update driver software... from the context menu.
- In the wizard, select Browse my computer for driver software.
- Select Let me pick from a list of device drivers on my computer.
- From the list of device classes, select Universal Serial Bus devices.
- The wizard displays WinUsb Device. Select it to load the driver.
If Universal Serial Bus devices does not appear in the list of device classes, then you need to install the driver by using a custom INF.The preceding procedure does not add a device interface GUID for an app (UWP app or Windows desktop app) to access the device. You must add the GUID manually by following this procedure.
Load the driver as described in the preceding procedure.
Generate a device interface GUID for your device, by using a tool such as guidgen.exe.
Find the registry key for the device under this key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetEnumUSB<VID_vvvv&PID_pppp>
Under the Device Parameters key, add a String registry entry named DeviceInterfaceGUID or a Multi-String entry named DeviceInterfaceGUIDs. Set the value to the GUID you generated in step 2.
Disconnect the device from the system and reconnect it to the same physical port.Note If you change the physical port then you must repeat steps 1 through 4.

Writing a custom INF for WinUSB installation
As part of the driver package, you provide an .inf file that installs Winusb.sys as the function driver for the USB device.
Hiti P510s Printer Driver Download
The following example .inf file shows WinUSB installation for most USB devices with some modifications, such as changing USB_Install in section names to an appropriate DDInstall value. You should also change the version, manufacturer, and model sections as necessary. For example, provide an appropriate manufacture's name, the name of your signed catalog file, the correct device class, and the vendor identifier (VID) and product identifier (PID) for the device.
Also notice that the setup class is set to 'USBDevice'. Vendors can use the 'USBDevice' setup class for devices that do not belong to another class and are not USB host controllers or hubs.
If you are installing WinUSB as the function driver for one of the functions in a USB composite device, you must provide the hardware ID that is associated with the function, in the INF. You can obtain the hardware ID for the function from the properties of the devnode in Device Manager. The hardware ID string format is 'USBVID_vvvv&PID_pppp'.
The following INF installs WinUSB as the OSR USB FX2 board's function driver on a x64-based system.
Starting in Windows 10, version 1709, the Windows Driver Kit provides InfVerif.exe that you can use to test a driver INF file to make sure there are no syntax issues and the INF file is universal. We recommened that you provide a universal INF. For more information, see Using a Universal INF File.
Only include a ClassInstall32 section in a device INF file to install a new custom device setup class. INF files for devices in an installed class, whether a system-supplied device setup class or a custom class, must not include a ClassInstall32 section.
Except for device-specific values and several issues that are noted in the following list, you can use these sections and directives to install WinUSB for any USB device. These list items describe the Includes and Directives in the preceding .inf file.
USB_Install: The Include and Needs directives in the USB_Install section are required for installing WinUSB. You should not modify these directives.
USB_Install.Services: The Include directive in the USB_Install.Services section includes the system-supplied .inf for WinUSB (WinUSB.inf). This .inf file is installed by the WinUSB co-installer if it isn't already on the target system. The Needs directive specifies the section within WinUSB.inf that contains information required to install Winusb.sys as the device's function driver. You should not modify these directives.Note Because Windows XP doesn't provide WinUSB.inf, the file must either be copied to Windows XP systems by the co-installer, or you should provide a separate decorated section for Windows XP.
USB_Install.HW: This section is the key in the .inf file. It specifies the device interface globally unique identifier (GUID) for your device. The AddReg directive sets the specified interface GUID in a standard registry value. When Winusb.sys is loaded as the device's function driver, it reads the registry value DeviceInterfaceGUIDs key and uses the specified GUID to represent the device interface. You should replace the GUID in this example with one that you create specifically for your device. If the protocols for the device change, create a new device interface GUID.
Note User-mode software must call SetupDiGetClassDevs to enumerate the registered device interfaces that are associated with one of the device interface classes specified under the DeviceInterfaceGUIDs key. SetupDiGetClassDevs returns the device handle for the device that the user-mode software must then pass to the WinUsb_Initialize routine to obtain a WinUSB handle for the device interface. For more info about these routines, see How to Access a USB Device by Using WinUSB Functions.
The following INF installs WinUSB as the OSR USB FX2 board's function driver on a x64-based system. The example shows INF with WDF coinstallers.
USB_Install.CoInstallers: This section, which includes the referenced AddReg and CopyFiles sections, contains data and instructions to install the WinUSB and KMDF co-installers and associate them with the device. Most USB devices can use these sections and directives without modification.
The x86-based and x64-based versions of Windows have separate co-installers.
Note Each co-installer has free and checked versions. Use the free version to install WinUSB on free builds of Windows, including all retail versions. Use the checked version (with the '_chk' suffix) to install WinUSB on checked builds of Windows.
Each time Winusb.sys loads, it registers a device interface that has the device interface classes that are specified in the registry under the DeviceInterfaceGUIDs key.
Note If you use the redistributable WinUSB package for Windows XP or Windows Server 2003, make sure that you don't uninstall WinUSB in your uninstall packages. Other USB devices might be using WinUSB, so its binaries must remain in the shared folder.
How to create a driver package that installs Winusb.sys
To use WinUSB as the device's function driver, you create a driver package. The driver package must contain these files:
- WinUSB co-installer (Winusbcoinstaller.dll)
- KMDF co-installer (WdfcoinstallerXXX.dll)
- An .inf file that installs Winusb.sys as the device's function driver. For more information, see Writing an .Inf File for WinUSB Installation.
- A signed catalog file for the package. This file is required to install WinUSB on x64 versions of Windows starting with Vista.
Note Make sure that the driver package contents meet these requirements:
- The KMDF and WinUSB co-installer files must be obtained from the same version of the Windows Driver Kit (WDK).
- The co-installer files must be obtained from the latest version of the WDK, so that the driver supports all the latest Windows releases.
- The contents of the driver package must be digitally signed with a Winqual release signature. For more info about how to create and test signed catalog files, see Kernel-Mode Code Signing Walkthrough on the Windows Dev Center - Hardware site.
Download the Windows Driver Kit (WDK) and install it.
Create a driver package folder on the machine that the USB device is connected to. For example, c:UsbDevice.
Copy the WinUSB co-installer (WinusbcoinstallerX.dll) from the WinDDKBuildNumberredistwinusb folder to the driver package folder.
The WinUSB co-installer (Winusbcoinstaller.dll) installs WinUSB on the target system, if necessary. The WDK includes three versions of the co-installer depending on the system architecture: x86-based, x64-based, and Itanium-based systems. They are all named WinusbcoinstallerX.dll and are located in the appropriate subdirectory in the WinDDKBuildNumberredistwinusb folder.
Copy the KMDF co-installer (WdfcoinstallerXXX.dll) from the WinDDKBuildNumberredistwdf folder to the driver package folder.
The KMDF co-installer (WdfcoinstallerXXX.dll) installs the correct version of KMDF on the target system, if necessary. The version of WinUSB co-installer must match the KMDF co-installer because KMDF-based client drivers, such as Winusb.sys, require the corresponding version of the KMDF framework to be installed properly on the system. For example, Winusbcoinstaller2.dll requires KMDF version 1.9, which is installed by Wdfcoinstaller01009.dll. The x86 and x64 versions of WdfcoinstallerXXX.dll are included with the WDK under the WinDDKBuildNumberredistwdf folder. The following table shows the WinUSB co-installer and the associated KMDF co-installer to use on the target system.
Use this table to determine the WinUSB co-installer and the associated KMDF co-installer.
WinUSB co-installer KMDF library version KMDF co-installer Winusbcoinstaller.dll Requires KMDF version 1.5 or later Wdfcoinstaller01005.dll
Wdfcoinstaller01007.dll
Wdfcoinstaller01009.dll
Winusbcoinstaller2.dll Requires KMDF version 1.9 or later Wdfcoinstaller01009.dll Winusbcoinstaller2.dll Requires KMDF version 1.11 or later WdfCoInstaller01011.dll Write an .inf file that installs Winusb.sys as the function driver for the USB device.
Create a signed catalog file for the package. This file is required to install WinUSB on x64 versions of Windows.
Attach the USB device to your computer.
Open Device Manager to install the driver. Follow the instructions on the Update Driver Software wizard and choose manual installation. You will need to provide the location of the driver package folder to complete the installation.
Related topics
WinUSB Architecture and Modules
Choosing a driver model for developing a USB client driver
How to Access a USB Device by Using WinUSB Functions
WinUSB Power Management
WinUSB Functions for Pipe Policy Modification
WinUSB Functions
WinUSB
Important
This topic is for programmers. If you are a customer experiencing USB problems, see Troubleshoot common USB problems
This topic lists the Microsoft-provided drivers for the supported USB device classes.
- Microsoft-provided drivers for USB-IF approved device classes.
- For composite devices, use USB Generic Parent Driver (Usbccgp.sys) that creates physical device objects (PDOs) for each function.
- For non-composite devices or a function of a composite device, use WinUSB (Winusb.sys).
If you are installing USB drivers: You do not need to download USB device class drivers. They are installed automatically. These drivers and their installation files are included in Windows. They are available in the WindowsSystem32DriverStoreFileRepository folder. The drivers are updated through Windows Update.
If you are writing a custom driver: Before writing a driver for your USB device, determine whether a Microsoft-provided driver meets the device requirements. If a Microsoft-provided driver is not available for the USB device class to which your device belongs, then consider using generic drivers, Winusb.sys or Usbccgp.sys. Write a driver only when necessary. More guidelines are included in Choosing a driver model for developing a USB client driver.
USB Device classes

USB Device classes are categories of devices with similar characteristics and that perform common functions. Those classes and their specifications are defined by the USB-IF. Each device class is identified by USB-IF approved class, subclass, and protocol codes, all of which are provided by the IHV in device descriptors in the firmware. Microsoft provides in-box drivers for several of those device classes, called USB device class drivers. If a device that belongs to a supported device class is connected to a system, Windows automatically loads the class driver, and the device functions with no additional driver required.
Hardware vendors should not write drivers for the supported device classes. Windows class drivers might not support all of the features that are described in a class specification. If some of the device's capabilities are not implemented by the class driver, vendors should provide supplementary drivers that work in conjunction with the class driver to support the entire range of functionality provided by the device.
For general information about USB-IF approved device classes see the USB Common Class Specification
The current list of USB class specifications and class codes is documented in the USB-IF Defined Class Code List.
Device setup classes
Windows categorizes devices by device setup classes, which indicate the functionality of the device.
Microsoft defines setup classes for most devices. IHVs and OEMs can define new device setup classes, but only if none of the existing classes apply. For more information, see System-Defined Device Setup Classes.
Two important device setup classes for USB devices are as follows:
USBDevice {88BAE032-5A81-49f0-BC3D-A4FF138216D6}: IHVs must use this class for custom devices that do not belong to another class. This class is not used for USB host controllers and hubs.
USB {36fc9e60-c465-11cf-8056-444553540000}: IHVs must not use this class for their custom devices. This is reserved for USB host controllers and USB hubs.
The device setup classes are different from USB device classes discussed earlier. For example, an audio device has a USB device class code of 01h in its descriptor. When connected to a system, Windows loads the Microsoft-provided class driver, Usbaudio.sys. In Device Manager, the device is shown under is Sound, video and game controllers, which indicates that the device setup class is Media.
Microsoft-provided USB device class drivers
| USB-IF class code | Device setup class | Microsoft-provided driver and INF | Windows support | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Audio (01h) | Media {4d36e96c-e325-11ce-bfc1-08002be10318} | Usbaudio.sys Wdma_usb.inf | Windows 10 for desktop editions (Home, Pro, Enterprise, and Education) Windows 10 Mobile Windows 8.1 Windows 8 Windows 7 Windows Server 2008 Windows Vista | Microsoft provides support for the USB audio device class by means of the Usbaudio.sys driver. For more information, see 'USBAudio Class System Driver' in Kernel-Mode WDM Audio Components. For more information about Windows audio support, see the Audio Device Technologies for Windows website. |
| Communications and CDC Control (02h) | ||||
| Ports {4D36E978-E325-11CE-BFC1-08002BE10318} | Usbser.sys Usbser.inf | Windows 10 for desktop editions Windows 10 Mobile | In Windows 10, a new INF, Usbser.inf, has been added that loads Usbser.sys automatically as the function driver. For more information, see USB serial driver (Usbser.sys) | |
| Modem {4D36E96D-E325-11CE-BFC1-08002BE10318} Note Supports Subclass 02h (ACM) | Usbser.sys Custom INF that references mdmcpq.inf | Windows 10 for desktop editions Windows 8.1 Windows 8 Windows 7 Windows Server 2008 Windows Vista | In Windows 8.1 and earlier versions, Usbser.sys is not automatically loaded. To load the driver, you need to write an INF that references the modem INF (mdmcpq.inf) and includes [Install] and [Needs] sections. Starting with Windows Vista, you can enable CDC and Wireless Mobile CDC (WMCDC) support by setting a registry value, as described in Support for the Wireless Mobile Communication Device Class. When CDC support is enabled, the USB Common Class Generic Parent Driver enumerates interface collections that correspond to CDC and WMCDC Control Models, and assigns physical device objects (PDO) to these collections. | |
| Net {4d36e972-e325-11ce-bfc1-08002be10318} Note Supports Subclass 0Eh (MBIM) | wmbclass.sys Netwmbclass.inf | Windows 10 for desktop editions Windows 8.1 Windows 8 | Starting in Windows 8, Microsoft provides the wmbclass.sys driver, for mobile broadband devices. See, MB Interface Model. | |
| HID (Human Interface Device) (03h) | HIDClass {745a17a0-74d3-11d0-b6fe-00a0c90f57da} | Hidclass.sys Hidusb.sys Input.inf | Windows 10 for desktop editions Windows 10 Mobile Windows 8.1 Windows 8 Windows 7 Windows Server 2008 Windows Vista | Microsoft provides the HID class driver (Hidclass.sys) and the miniclass driver (Hidusb.sys) to operate devices that comply with the USB HID Standard. For more information, see HID Architecture and Minidrivers and the HID class driver. For further information about Windows support for input hardware, see the Input and HID - Architecture and Driver Support website. |
| Physical (05h) | - | - | - | Recommended driver: WinUSB (Winusb.sys) |
| Image (06h) | Image {6bdd1fc6-810f-11d0-bec7-08002be2092f} | Usbscan.sys Sti.inf | Windows 10 for desktop editions Windows 8.1 Windows 8 Windows 7 Windows Server 2008 Windows Vista | Microsoft provides the Usbscan.sys driver that manages USB digital cameras and scanners for Windows XP and later operating systems. This driver implements the USB component of the Windows Imaging Architecture (WIA). For more information about WIA, see Windows Image Acquisition Drivers and the Windows Imaging Component website. For a description of the role that Usbscan.sys plays in the WIA, see WIA Core Components. |
| Printer (07h) | USB Note Usbprint.sys enumerates printer devices under the device set up class: Printer {4d36e979-e325-11ce-bfc1-08002be10318}. | Usbprint.sys Usbprint.inf | Windows 10 for desktop editions Windows 8.1 Windows 8 Windows 7 Windows Server 2008 Windows Vista | Microsoft provides the Usbprint.sys class driver that manages USB printers. For information about implementation of the printer class in Windows, see the Printing - Architecture and Driver Support website. |
| Mass Storage (08h) | ||||
| USB | Usbstor.sys | Windows 10 for desktop editions Windows 10 Mobile Windows 8.1 Windows 8 Windows 7 Windows Server 2008 Windows Vista | Microsoft provides the Usbstor.sys port driver to manage USB mass storage devices with Microsoft's native storage class drivers. For an example device stack that is managed by this driver, see Device Object Example for a USB Mass Storage Device. For information about Windows storage support, see the Storage Technologies website. | |
| SCSIAdapter {4d36e97b-e325-11ce-bfc1-08002be10318} | SubClass (06) and Protocol (62) Uaspstor.sys Uaspstor.inf | Windows 10 for desktop editions Windows 10 Mobile Windows 8.1 Windows 8 | Uaspstor.sys is the class driver for SuperSpeed USB devices that support bulk stream endpoints. For more information see: | |
| Hub (09h) | USB {36fc9e60-c465-11cf-8056-444553540000} | |||
| Usbhub.sys Usb.inf | Windows 10 for desktop editions Windows 10 Mobile Windows 8.1 Windows 8 Windows 7 Windows Server 2008 Windows Vista | Microsoft provides the Usbhub.sys driver for managing USB hubs. For more information about the relationship between the hub class driver and the USB stack, see USB host-side drivers in Windows. | ||
| Usbhub3.sys Usbhub3.inf | Windows 10 for desktop editions Windows 8.1 Windows 8 | Microsoft provides the Usbhub3.sys driver for managing SuperSpeed (USB 3.0) USB hubs. The driver is loaded when a SuperSpeed hub is attached to an xHCI controller. See USB host-side drivers in Windows. | ||
| CDC-Data (0Ah) | - | - | - | Recommended driver: WinUSB (Winusb.sys) |
| Smart Card (0Bh) | SmartCardReader {50dd5230-ba8a-11d1-bf5d-0000f805f530} | |||
| Usbccid.sys (Obsolete) | Windows 10 for desktop editions Windows 7 Windows Server 2008 Windows Vista | Microsoft provides the Usbccid.sys mini-class driver to manage USB smart card readers. For more information about smart card drivers in Windows, see Smart Card Design Guide. Note that for Windows Server 2003, Windows XP, and Windows 2000, special instructions are required for loading this driver because it might have been released later than the operating system. Note Usbccid.sys driver has been replaced by UMDF driver, WUDFUsbccidDriver.dll. | ||
| WUDFUsbccidDriver.dll WUDFUsbccidDriver.inf | Windows 8.1 Windows 8 | WUDFUsbccidDriver.dll is a user-mode driver for USB CCID Smart Card Reader devices. | ||
| Content Security (0Dh) | - | - | - | Recommended driver: USB Generic Parent Driver (Usbccgp.sys). Some content security functionality is implemented in Usbccgp.sys. See Content Security Features in Usbccgp.sys. |
| Video (0Eh) | Image {6bdd1fc6-810f-11d0-bec7-08002be2092f} | Usbvideo.sys Usbvideo.inf | Windows 10 for desktop editions Windows Vista | Microsoft provides USB video class support by means of the Usbvideo.sys driver. For more information, see 'USB Video Class Driver' under AVStream Minidrivers. Note that for Windows XP, special instructions are required for loading this driver because it might have been released later than the operating system. |
| Personal Healthcare (0Fh) | - | - | - | Recommended driver: WinUSB (Winusb.sys) |
| Audio/Video Devices (10h) | - | - | - | - |
| Diagnostic Device (DCh) | - | - | - | Recommended driver: WinUSB (Winusb.sys) |
| Wireless Controller (E0h) Note Supports Subclass 01h and Protocol 01h | Bluetooth {e0cbf06c-cd8b-4647-bb8a-263b43f0f974} | Bthusb.sys Bth.inf | Windows 10 for desktop editions Windows 10 Mobile Windows 8.1 Windows 8 Windows 7 Windows Vista | Microsoft provides the Bthusb.sys miniport driver to manage USB Bluetooth radios. For more information, see Bluetooth Design Guide. |
| Miscellaneous (EFh) | Net {4d36e972-e325-11ce-bfc1-08002be10318} Note Supports SubClass 04h and Protocol 01h | Rndismp.sys Rndismp.inf | Windows 10 for desktop editions Windows 8.1 Windows 8 Windows 7 Windows Vista | Prior to Windows Vista, support for CDC is limited to the RNDIS-specific implementation of the Abstract Control Model (ACM) with a vendor-unique protocol (bInterfaceProtocol) value of 0xFF. The RNDIS facility centers the management of all 802-style network cards in a single class driver, Rndismp.sys. For a detailed discussion of remote NDIS, see Overview of Remote NDIS. The mapping of remote NDIS to USB is implemented in the Usb8023.sys driver. For further information about networking support in Windows, see the Networking and Wireless Technologies website. |
| Application Specific (FEh) | - | - | - | Recommended driver: WinUSB (Winusb.sys) |
| Vendor Specific (FFh) | - | - | Windows 10 for desktop editions Windows 10 Mobile | Recommended driver: WinUSB (Winusb.sys) |
Hiti Usb Devices Driver Download For Windows Xp
Related topics
